Sustainable electronics lifecycle reduces e-waste generation impact
Introduction
The rapid evolution of laptops and mobile devices has transformed modern life, enabling faster communication, remote work, and digital convenience. However, this technological growth has also triggered a global crisis — electronic waste (e-waste). Discarded laptops and mobiles now represent one of the fastest-growing waste streams worldwide. Addressing this issue requires a sustainable electronics lifecycle, which focuses on responsible design, usage, reuse, recycling, and disposal. When implemented effectively, a sustainable electronics lifecycle significantly reduces e-waste generation impact, conserving resources and protecting the environment.
This article explores how sustainable practices across the lifecycle of laptops and mobiles can reduce e-waste, minimize pollution, and support a circular economy.
Understanding the Electronics Lifecycle
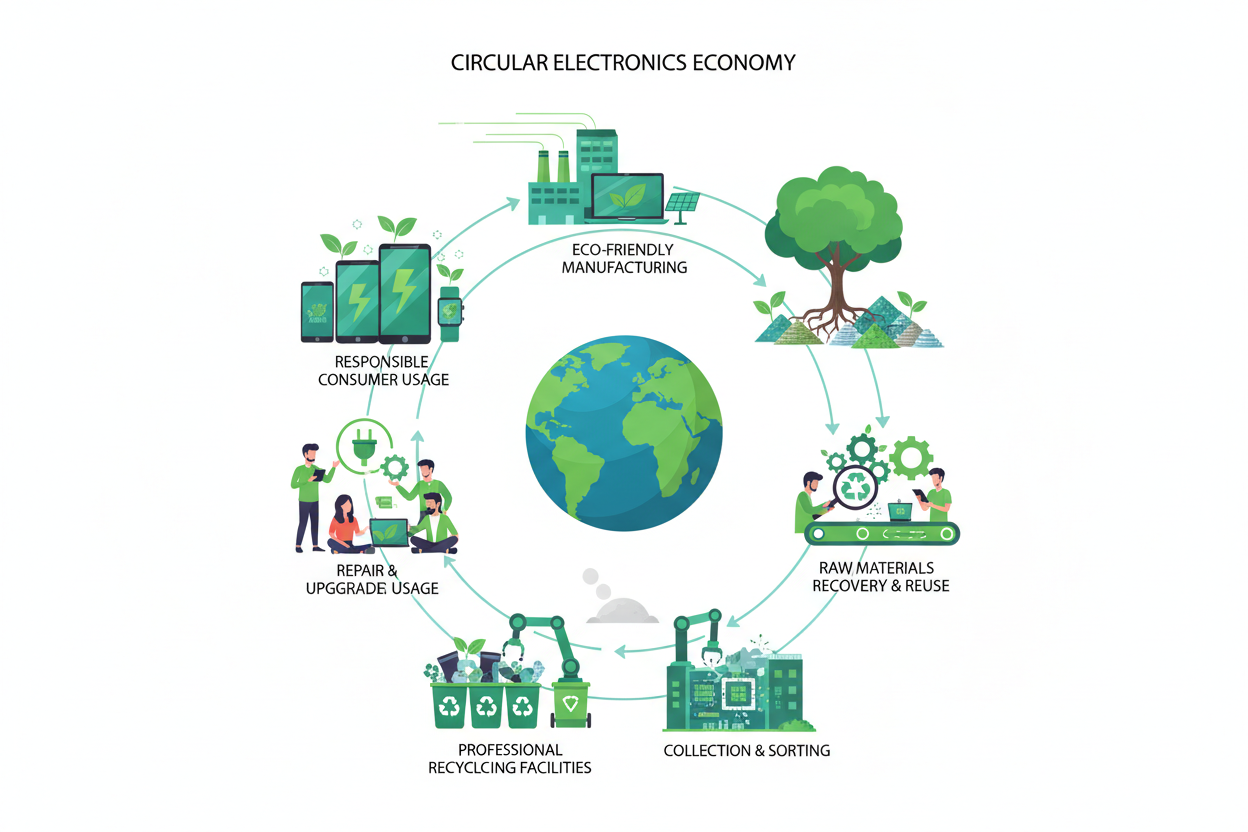
The electronics lifecycle refers to the complete journey of a device — from raw material extraction to manufacturing, usage, reuse, and final disposal. In conventional models, electronics often follow a linear lifecycle: make, use, and discard. This model leads to excessive resource extraction and uncontrolled e-waste generation.
A sustainable electronics lifecycle, on the other hand, adopts a circular approach, ensuring devices remain in use for as long as possible and are responsibly recycled at the end of life. This shift is particularly crucial for laptops and mobiles, which contain hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and lithium.
Why E-Waste from Laptops and Mobiles Is a Growing Concern
The global dependence on technology has shortened device replacement cycles. Consumers frequently upgrade smartphones every two to three years and laptops every four to five years. This trend contributes to millions of tons of e-waste annually.
Key Environmental Risks of E-Waste
-
Toxic chemicals leaching into soil and water
-
Air pollution from informal recycling practices
-
Loss of valuable materials like gold, copper, and rare earth metals
-
Increased carbon emissions from manufacturing new devices
Without a sustainable electronics lifecycle, discarded laptops and mobiles become a serious threat to ecosystems and public health.
Sustainable Design: The Foundation of E-Waste Reduction
Sustainability begins at the design stage. Manufacturers play a vital role in reducing e-waste by designing products that last longer and are easier to repair.
Key Sustainable Design Practices
-
Modular components for easy repair and upgrades
-
Durable materials that extend product lifespan
-
Reduced use of toxic substances
-
Energy-efficient processors and displays
By embracing sustainable design, manufacturers of laptops and mobiles reduce premature device obsolescence and encourage long-term usage, directly lowering e-waste generation.
Responsible Manufacturing and Material Sourcing
The manufacturing phase contributes significantly to the environmental footprint of electronics. Mining raw materials consumes energy, water, and land while emitting greenhouse gases.
A sustainable electronics lifecycle prioritizes:
-
Ethically sourced raw materials
-
Recycled metals and plastics
-
Reduced packaging waste
-
Lower carbon emissions during production
When manufacturers incorporate recycled components into laptops and mobiles, fewer natural resources are extracted, and less waste is generated.
Extending Device Lifespan Through Smart Usage
Consumers play a critical role in minimizing e-waste through responsible usage. Extending the lifespan of laptops and mobiles reduces the demand for new devices and cuts down on waste.
Tips for Sustainable Device Usage
-
Use protective cases and screen guards
-
Keep software updated for performance optimization
-
Replace batteries instead of discarding devices
-
Avoid unnecessary upgrades
By practicing mindful consumption, users actively support a sustainable electronics lifecycle and help reduce e-waste impact.
Repair, Refurbishment, and Reuse
One of the most effective ways to reduce e-waste is through repair and refurbishment. Many laptops and mobiles are discarded due to minor faults that can be easily fixed.
Benefits of Repair & Refurbishment
-
Extends product lifespan
-
Reduces environmental pollution
-
Creates green jobs
-
Makes technology affordable
Refurbished laptops and mobiles offer a sustainable alternative for students, startups, and budget-conscious users. Encouraging repair culture is essential for minimizing e-waste.
Recycling and Resource Recovery
Even when devices reach the end of their usable life, responsible recycling ensures valuable materials are recovered safely.
Importance of E-Waste Recycling
-
Prevents toxic materials from harming the environment
-
Recovers precious metals like gold, silver, and copper
-
Reduces energy consumption compared to mining
-
Supports circular economy principles
Certified e-waste recyclers dismantle laptops and mobiles safely, ensuring hazardous substances are handled responsibly and reusable materials are recovered.
Corporate Responsibility and Sustainable Innovation
Technology companies are increasingly adopting sustainability goals. Many brands now offer:
-
Trade-in programs
-
Take-back schemes
-
Carbon-neutral manufacturing initiatives
Such programs encourage users to return old laptops and mobiles instead of discarding them improperly. Corporate responsibility is a crucial pillar of a sustainable electronics lifecycle.
Environmental and Social Benefits of Sustainable Electronics Lifecycle
Implementing sustainable practices across the electronics lifecycle delivers long-term benefits.
Environmental Benefits
-
Reduced landfill waste
-
Lower carbon emissions
-
Conservation of natural resources
Social Benefits
-
Safer recycling conditions
-
Job creation in green industries
-
Improved public health
By reducing e-waste generation impact, sustainable electronics practices create a healthier planet for future generations.
Future of Sustainable Electronics
The future of electronics lies in circular economy models, where products are designed to be reused, repaired, and recycled continuously. Innovations such as biodegradable materials, modular smartphones, and AI-driven recycling systems will further strengthen sustainability efforts.
For laptops and mobiles, embracing sustainability is no longer optional — it is a necessity to combat the growing e-waste crisis.
Conclusion
A sustainable electronics lifecycle is one of the most effective solutions to reduce e-waste generation impact, especially from laptops and mobiles. From eco-friendly design and responsible manufacturing to extended usage, repair, and recycling, every stage plays a crucial role. Consumers, manufacturers, and governments must work together to shift from a linear to a circular approach.
By making conscious choices today, we can reduce environmental damage, conserve resources, and build a sustainable digital future.
FAQs
Q.1. What is a sustainable electronics lifecycle?
It is an approach that focuses on designing, using, reusing, and recycling electronics responsibly to reduce e-waste.
Q.2. Why are laptops and mobiles major contributors to e-waste?
Short replacement cycles and improper disposal make laptops and mobiles a leading source of electronic waste.
Q.3. How does repairing devices reduce e-waste?
Repairing extends device lifespan, reducing the need for new products and minimizing waste.
Q.4. What role does recycling play in e-waste management?
Recycling safely recovers valuable materials and prevents environmental pollution.
Q.5. How can consumers support sustainable electronics?
By using devices longer, repairing instead of replacing, and recycling through certified programs.