What Is E-Waste Recycling and How Is It Done?
Introduction
Electronic waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world today. Every home uses mobile phones, laptops, tablets and many electronic devices that eventually become outdated or stop working. When these devices are thrown away, they become e-waste. Proper e-waste recycling is important because it protects the environment, saves resources, and reduces pollution. Many people do not know what e-waste recycling means or how this process works. This blog explains the concept of e-waste recycling, why it is important, and how the recycling process takes place in a simple and clear way.
What Is E-Waste?
E-waste refers to all discarded electronic and electrical devices. These devices may be old, broken, or no longer in use. Examples include mobile phones, computers, washing machines, chargers, cables, batteries, and printers. As technology grows fast, e-waste also increases. Many people change their phones every year. Companies release new laptop models quickly. This leads to more e-waste every day.
E-waste contains valuable materials like copper, silver, gold, and aluminum. It also contains harmful chemicals like lead and mercury. If e-waste is not handled properly, it can pollute the air, water, and soil. That is why proper e-waste recycling is necessary.
Why Is E-Waste Recycling Important?
E-waste recycling is important for the environment and for human health. Here are the main reasons:
1. Protects the Environment
E-waste contains toxic substances. When dumped in landfills, these toxins can leak into the soil and water. Proper e-waste recycling prevents this pollution.
2. Saves Natural Resources
E-waste has valuable metals. Recycling these materials reduces the need for mining. Mining uses a lot of energy and harms the earth. Recycling saves energy and protects natural resources.
3. Reduces Greenhouse Gases
Manufacturing new devices uses energy. Recycling reduces the need to produce new materials, which lowers carbon emissions.
4. Supports the Circular Economy
Recycling encourages repairing, reusing, and recovering materials. This creates a sustainable system where products stay in use for a long time.
5. Creates Job Opportunities
The e-waste recycling industry creates jobs in collection, sorting, processing, and manufacturing.
How Is E-Waste Recycling Done? (Step-by-Step Process)
E-waste recycling involves many scientific and mechanical processes. Below is the complete step-by-step explanation in simple words.
1. Collection and Transportation
The first step is collecting e-waste from homes, offices, shops, and recycling centers. Collection boxes are placed at malls, showrooms, and public places. Special teams collect and transport e-waste to recycling plants. Safe transportation is important because some components are fragile and hazardous.
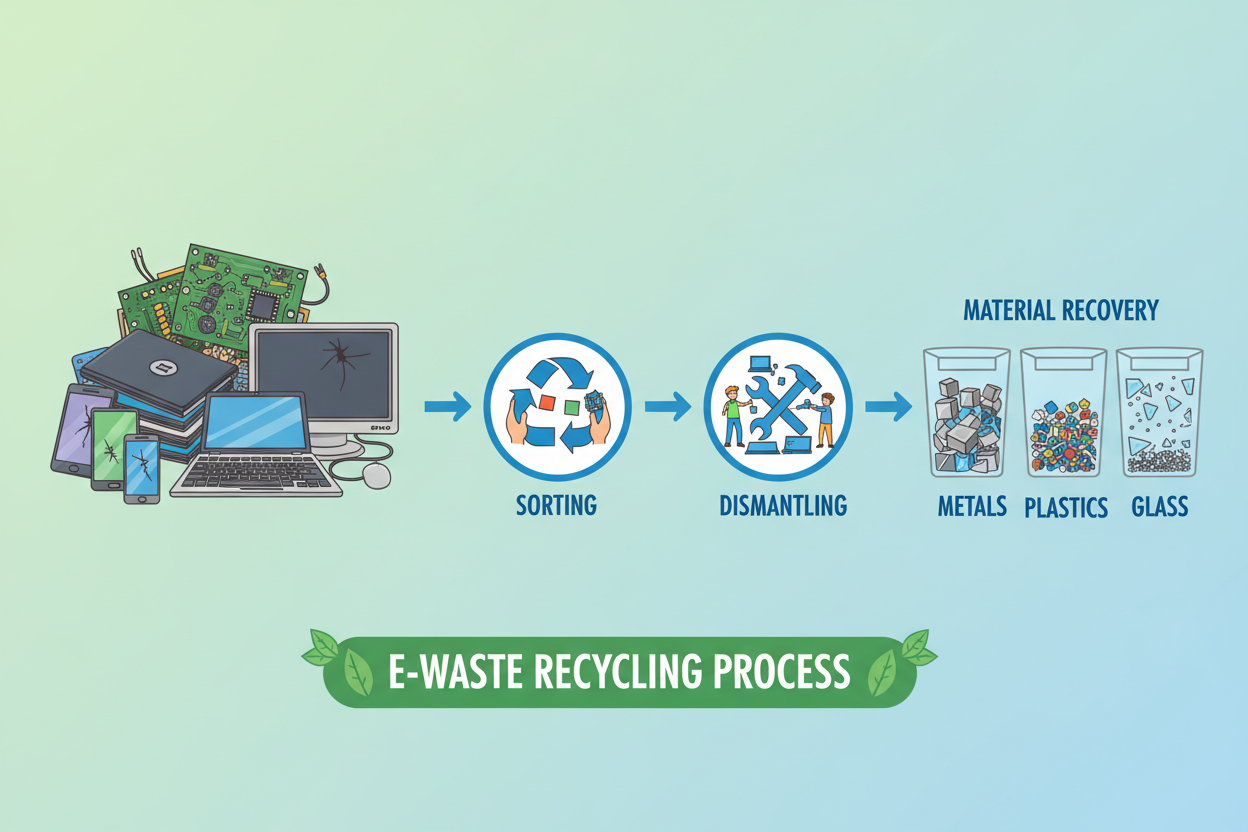
2. Sorting and Categorization
At the recycling facility, e-waste is sorted by type. Items like phones, laptops, batteries, and home appliances are separated. This makes the next steps easier. Manual sorting helps identify reusable parts or devices that can be repaired.
3. Data Destruction / Secure Wiping
Before recycling, all personal data is permanently removed from devices. Hard drives and memory cards are wiped or physically destroyed to protect privacy.
4. Dismantling
Technicians dismantle the devices manually. They remove parts like screens, batteries, circuit boards, plastic covers, wires, and metal frames. Hazardous components like lithium batteries are separated and handled safely.
5. Shredding
Large pieces are put into shredding machines. These machines break the e-waste into smaller fragments. Shredding allows materials to be separated more easily.
6. Material Separation
Different technologies are used to separate materials such as:
Magnetic Separation
Magnets remove iron and steel materials.
Density Separation
Lighter materials like plastic float, while heavier metals sink.
Air Separation
Air blowers separate dust and light particles.
Optical Sorting
Sensors help separate materials based on color and type.
Through these steps, valuable materials like copper, aluminum, gold, and plastics are recovered.
7. Chemical Processing
Some materials require chemical treatment to extract valuable metals. For example:
-
Gold and silver are removed from circuit boards using chemical solutions.
-
Copper is extracted from wires by chemical or mechanical stripping.
These processes must be done safely to avoid pollution.
8. Refining and Purification
Recovered metals are refined to remove impurities. They are melted, purified, and processed into reusable metal blocks.
9. Recycling of Plastics and Glass
Plastic and glass parts are cleaned and melted. They are used to make new products like plastic containers, tiles, or glass panels.
10. Safe Disposal of Residue
Some leftover materials cannot be recycled. These are disposed of safely using approved waste management methods to avoid environmental harm.
Benefits of E-Waste Recycling
1. Reduces Environmental Pollution
Recycling prevents toxic chemicals from entering the environment.
2. Saves Energy
Recycling metals uses less energy than producing new metals.
3. Conserves Resources
Recycling reduces the need for mining.
4. Encourages Sustainable Development
Recycling promotes a cleaner and greener planet.
5. Reduces Landfill Waste
Less e-waste ends up in dumpsites.
Simple Tips to Reduce E-Waste at Home
You can help reduce e-waste in simple ways:
-
Use devices for a longer time.
-
Repair instead of replace.
-
Donate old but working devices.
-
Buy energy-efficient and durable products.
-
Avoid unnecessary gadgets.
-
Recycle old devices responsibly.
-
Use certified recycling centers.
Global E-Waste Challenges
The world generates millions of tons of e-waste every year. Many countries lack proper recycling facilities. Illegal dumping and informal recycling are common in some regions. These practices harm workers and the environment. There is a strong need for:
-
Government rules
-
Public awareness
-
Investment in recycling facilities
-
Safe recycling systems
Future of E-Waste Recycling
The future of e-waste recycling is bright. Many companies are now using eco-friendly designs. New technologies like AI-based sorting, robotic dismantling, and advanced chemical recovery systems are improving recycling efficiency. Governments are promoting the circular economy by encouraging repair, reuse, and responsible recycling. Consumers are also becoming more aware of environmental issues.
Conclusion
E-waste is a global challenge, but responsible recycling can solve many problems. E-waste recycling is the process of collecting, dismantling, and extracting valuable materials from discarded devices. It protects the environment, saves resources, and supports sustainability. Every person can play a role in reducing e-waste by repairing devices, reusing gadgets, and recycling old electronics properly. The world needs strong systems, modern recycling technologies, and public awareness to manage e-waste effectively. With collective action, we can create a cleaner and greener future for the next generation.
FAQs
1. What is e-waste?
E-waste is discarded electronic devices like phones, laptops and appliances.
2. Why is e-waste harmful?
It contains toxic chemicals that can pollute soil, air, and water.
3. What is e-waste recycling?
It is the process of collecting and processing old electronics to recover useful materials.
4. How can I reduce e-waste?
Use devices longer, repair old gadgets, donate working items, and recycle responsibly.
5. Where should I dispose of e-waste?
At certified recycling centers or government-approved collection points.





