Uncovering the Hidden Impact of E-Waste on Our Planet
Introduction
E-waste is growing faster than any other waste stream in the world, and the hidden impact of this problem is far greater than most people realize. Every year, millions of old laptops, mobiles, smartwatches, and electronic accessories end up in landfills, causing serious environmental harm. Toxic materials leak into soil and water, while the energy needed to produce new devices increases carbon emissions. Many people replace gadgets quickly without thinking of the consequences. By understanding the hidden impact of E-waste, we can take better steps to reduce damage and promote sustainability. This blog explains why responsible disposal and refurbished choices matter.
What Exactly Is E-Waste and Why It Matters
E-waste includes every electronic product we throw away. This includes old laptops, broken mobiles, unused smartwatches, chargers, keyboards, tablets, and batteries. Most of these items contain toxic materials like lead, mercury, cadmium, and flame-retardant chemicals. When these substances reach the soil or water, they create long-term contamination that affects humans, animals, and plants. E-waste is dangerous because it does not break down naturally. The parts remain harmful for hundreds of years. Many countries do not have strong recycling systems, so e-waste piles up in landfills or informal dump sites. This creates a growing environmental risk.
The Hidden Cost of Upgrading Devices Too Often
Technology companies launch new models every year. Many people replace their mobiles, laptops, and smartwatches even when the old ones still work. This creates unnecessary waste. When production of new devices increases, energy consumption and raw-material mining also increase. Metals like lithium, cobalt, copper, and gold must be extracted from the earth. Mining these materials harms forests, rivers, and ecosystems. These hidden costs are not visible when people buy a new gadget, but they add significantly to global pollution. Choosing refurbished devices or extending the lifespan of current devices can reduce this waste.
How E-Waste Affects Air Quality
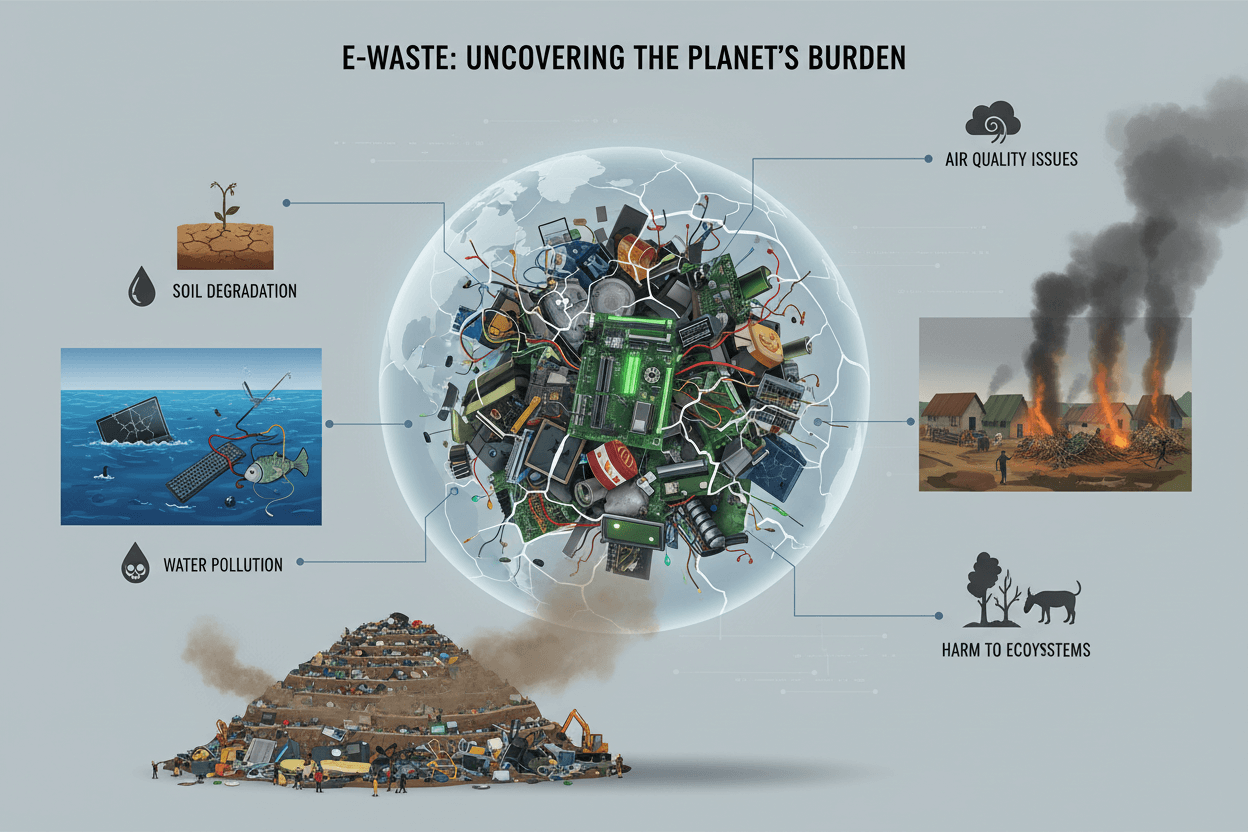
When e-waste is burned in open areas, toxic fumes are released. Burning plastic components from old phones, laptops, and watches produces dioxins and furans, which are extremely harmful chemicals. Workers in informal recycling sites often inhale these toxic fumes every day. These gases pollute the air and spread respiratory diseases. Even small quantities can cause long-term health effects like asthma, cancer, and neurological issues. The hidden impact is that this air pollution does not stay in one location. Winds can carry dangerous chemicals to nearby communities, affecting large populations.
Soil and Water Contamination from E-Waste
When old electronic items are dumped in landfills, the toxic metals slowly leak out. Lead contaminates soil, mercury contaminates water, and cadmium spreads through groundwater. Crops grown in contaminated soil absorb these metals. This eventually enters the human food chain. Water sources near large dumping sites become unsafe for drinking. Many countries experience these problems daily because they receive e-waste from around the world. What many people do not realise is that one small phone battery can contaminate thousands of liters of water. This makes e-waste a silent but powerful environmental threat.
The Energy Footprint Behind Every New Device
To produce a single new laptop or mobile phone, manufacturers need large amounts of energy. Factories run for long hours. Water is used in large quantities for cleaning and cooling processes. Transportation of devices across countries increases carbon emissions. When people throw away old devices quickly, companies must produce more, increasing the overall carbon footprint. The hidden impact is that the energy used before the product reaches the buyer is much more than the energy used during the device’s lifetime. Choosing refurbished devices helps reduce this energy demand.
The Role of Smartwatches in Growing E-Waste
Smartwatches are small but contribute significantly to e-waste. They contain plastic, metal, tiny batteries, sensors, and display panels. Many users upgrade their smartwatch every year for new features. But the small size of smartwatches makes them harder to recycle. The batteries can cause fires in waste-processing plants if not handled safely. Disposing of smartwatches in household bins is dangerous. Recycling centers must treat them like other electronic devices. Using the same smartwatch for a few more years reduces environmental impact greatly.
Laptops: The Largest Contributor to Toxic E-Waste
Laptops contain some of the most harmful electronic components. They have large batteries, circuit boards, processors, and metal parts. When laptops become outdated, many people throw them away instead of repairing them. The hidden impact of laptop waste is much greater because a single laptop contains more toxic materials than a mobile phone. Heavy metals inside the motherboard and battery can leak into the environment for years. Refurbishing old laptops or upgrading RAM and storage can extend their life by 3–5 years, leading to less waste.
Mobile Phones: The Fastest-Growing E-Waste Category
Mobile phones are replaced faster than any other gadget. People switch models for better cameras, battery life, or new features. This rapid replacement makes mobile phones the fastest-growing source of E-waste worldwide. Old phones contain precious metals that can be recovered through recycling. But only a small percentage is actually recycled. Most end up in drawers or landfills. The hidden impact is that when phones are not recycled, we lose valuable materials like gold and copper that could be reused. This increases the need for more mining.
Batteries: Small in Size, Big in Pollution
The lithium-ion batteries inside laptops, mobiles, and smartwatches are extremely harmful when not disposed of correctly. They can leak chemicals like electrolytes, cobalt, and lithium. Damaged batteries can catch fire easily. Many fires in recycling centers are caused by improperly disposed batteries. Batteries must always be recycled separately. The environmental risk of batteries is hidden because people do not see the immediate damage. But the long-term effects are severe and lasting.
How Refurbished Devices Help Reduce E-Waste
Refurbished devices are repaired, tested, and restored to good condition. Buying a refurbished mobile, laptop, or smartwatch reduces the need for new production. This lowers energy use, reduces mining of raw materials, and cuts carbon emissions. Refurbished devices are affordable, reliable, and eco-friendly. Many companies now promote refurbished models as part of their sustainability strategy. When consumers choose refurbished products, they actively reduce E-waste and help protect the planet. Choosing refurbished is one of the most powerful ways to reduce environmental impact.
Global E-Waste Statistics (Simple Explanation)
-
The world produces over 50 million tons of E-waste every year.
-
Only 15–20% of this waste is properly recycled.
-
Mobile phones and laptops form the largest part of small electronic waste.
-
E-waste is increasing by 3–4% each year, faster than any other waste stream.
-
Most E-waste is shipped to developing countries for low-cost recycling.
These numbers show how serious the problem is and why urgent action is necessary.
Health Risks Caused by E-Waste
People working in informal recycling sites face the highest risk. They handle toxic materials with bare hands. Children in many countries help sort waste, exposing them to dangerous chemicals. Long-term exposure leads to brain damage, skin diseases, hormonal imbalance, and kidney problems. Communities near dumping sites breathe polluted air and drink contaminated water. Many health problems also appear years later, making the connection to E-waste hard to detect. This is why the health impact is called “hidden”.
Why Proper Recycling Makes a Big Difference
Proper recycling of laptops, mobiles, smartwatches, and batteries allows valuable materials to be recovered. Metals like gold, silver, copper, and aluminum can be reused. Safe recycling prevents toxic chemicals from reaching the environment. Recycling centers follow strict safety rules. Users must deposit old electronics only at certified recycling points. Even one recycled device can prevent large amounts of pollution. If millions of people recycle responsibly, the positive environmental effect will be huge.
How Consumers Can Reduce E-Waste
Here are easy ways everyone can help reduce E-waste:
-
Use devices for a longer time.
-
Repair instead of replacing.
-
Buy refurbished laptops and mobiles.
-
Donate usable devices to others.
-
Recycle batteries separately.
-
Avoid throwing electronics in household bins.
-
Choose brands with strong recycling programs.
Small actions, when repeated by many people, make a big impact.
Future Solutions for Reducing E-Waste
Companies are working on sustainable solutions such as:
-
Designing devices that last longer.
-
Making batteries easier to replace.
-
Using recyclable materials in new products.
-
Promoting refurbished and second-hand markets.
-
Building modern recycling plants.
-
Encouraging consumers to recycle responsibly.
A sustainable future is possible if everyone plays a role — manufacturers, consumers, and governments.
Conclusion
The hidden impact of E-waste is one of the most serious environmental challenges of our time. Laptops, mobiles, smartwatches, and accessories create toxic waste when not disposed of properly. This pollution affects air, water, soil, and human health. The solution is simple but powerful — reduce, reuse, repair, refurbish, and recycle. When consumers choose refurbished devices, extend the lifespan of gadgets, and dispose of electronics responsibly, the environment benefits immediately. Awareness is the first step. Action must follow. Together, we can reduce E-waste and protect our planet for future generations.
5 Short FAQs
Q.1. What is E-waste?
E-waste is discarded electronic devices like mobiles, laptops, smartwatches, and batteries.
Q.2. Why is E-waste harmful?
It contains toxic chemicals that pollute air, water, and soil.
Q.3. How can I reduce E-waste at home?
Use devices longer, repair them, recycle properly, and choose refurbished products.
Q.4. What happens if batteries are not recycled?
They leak harmful chemicals and can cause fires in landfills or recycling centers.
Q.5. Are refurbished devices safe?
Yes, high-quality refurbished devices are tested, repaired, and certified for reliable use.