What Is E-Waste Recycling and How Is it Done?
Introduction
Electronic waste, also called E-waste, is one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world. Every year, millions of people replace their laptops, phones, and smartwatches with newer models. When old devices are thrown away, they become E-waste, which can harm the environment. Toxic materials like lead, mercury, and chemicals leak into soil and water when these products end up in landfills. This is why E-waste recycling is very important. E-waste recycling helps recover useful materials and reduces pollution. It also supports a sustainable waste management system for the future.
What Is E-Waste Recycling?
E-waste recycling is the process of collecting, separating, and treating old electronic products so they can be reused, refurbished, or turned into raw materials. It prevents harmful substances from entering the environment and saves valuable resources.
Old laptops, phones, and smartwatches contain plastics, metals, glass, and even small amounts of gold, silver, and copper. Instead of letting these materials go to waste, recycling helps extract them in a safe and responsible way.
This process supports sustainable waste solutions and reduces the pressure on mining natural resources.
Why E-Waste Recycling Matters Today
The use of electronic devices is increasing every year. People upgrade their mobile phones frequently. Laptops become outdated quickly. New smartwatches launch almost every few months. This fast replacement cycle creates a huge pile of discarded gadgets.
If this E-waste is not handled properly, it leads to soil pollution, water pollution, and health risks. Recycling saves materials, energy, and the environment.
Many countries now encourage people to recycle their electronics instead of throwing them away. This improves sustainable waste management and helps protect the planet from long-term damage.
What Types of E-Waste Need Recycling?
1. Laptops
Laptops contain batteries, circuit boards, screens, and metal bodies. Their components can be harmful if dumped. But they also have valuable metals that can be recovered.
2. Mobile Phones
Phones contain plastic, aluminum, lithium batteries, copper wiring, and small amounts of precious metals. Recycling helps extract these materials and reduces mining activities.
3. Smartwatches
Smartwatches are small but contain batteries, sensors, and chips. They must be recycled safely to avoid pollution.
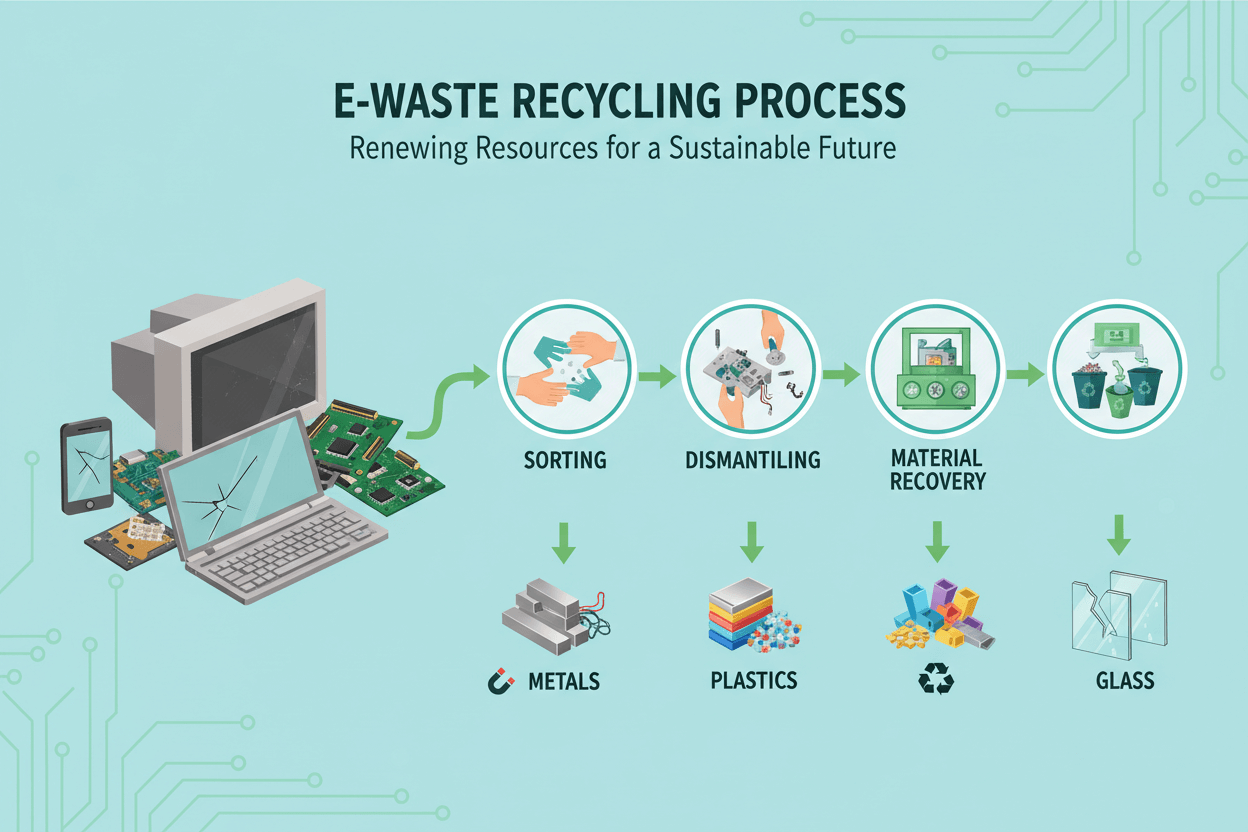
How E-Waste Recycling Is Done (Step-by-Step Process)
Collection of Old Electronics
The recycling process begins with collection. People can drop their old laptops, phones, and smartwatches at recycling centers, retail collection points, or government-approved facilities. Some brands also offer buy-back or exchange programs to encourage proper disposal. Collection ensures that E-waste is handled safely and does not enter landfills or household trash.
Sorting and Categorizing the Devices
After collection, the E-waste is sorted into categories such as laptops, phones, smartwatches, and accessories. Sorting is important because each device contains different materials and needs different recycling methods. Technicians check whether any devices can be repaired or refurbished instead of being broken down. Refurbished devices can be reused, which supports sustainable waste reduction.
Data Wiping and Secure Handling
Before recycling, all personal data must be removed. Recyclers wipe the storage drives of laptops and phones. This step protects user privacy and ensures that no sensitive information remains. Data wiping is a mandatory process in responsible E-waste recycling.
Manual Disassembly
Workers manually dismantle devices by removing batteries, screens, speakers, processors, and motherboards. This step is crucial because many parts, especially lithium batteries, must be handled with care. Manual disassembly helps separate reusable components and makes it easier to extract materials later.
Shredding the Remaining Parts
After removing reusable or hazardous components, the rest of the device goes into a shredding machine. Shredding breaks the device into tiny pieces so that metals, plastics, and glass can be separated efficiently. Shredding increases the recycling speed and makes sorting easier.
Magnetic and Non-Magnetic Separation
Shredded materials pass through magnetic separators that pull out iron and steel. Non-magnetic metals like aluminum and copper are collected separately. This separation helps recyclers extract valuable metals from the device.
Use of Water and Air Separation Systems
Light materials like plastic and glass are separated using water-based or air-based systems.
Heavy metals sink, and lighter materials float. Air flow systems blow lighter particles away, making separation fast and efficient. This step helps produce cleaner recyclable materials.
Extraction of Precious Metals
Circuit boards from laptops, phones, and watches contain small amounts of gold, silver, palladium, and copper. Recyclers use chemical or heat-based processes to remove these precious metals safely. Extracted metals re-enter the manufacturing chain, reducing the need for mining. This supports global sustainable waste and responsible resource usage.
Recycling Batteries Safely
Batteries are some of the most dangerous components in E-waste. Lithium-ion batteries from laptops, phones, and watches can explode if not handled properly. Recyclers remove and process these batteries separately to prevent fire hazards. The valuable materials inside batteries, like lithium and cobalt, are also recovered for reuse.
Preparing Recycled Materials for Reuse
Once all materials are separated, they are cleaned and processed into raw forms.
These materials are then sent to manufacturing industries to create new products.
Recycled metals, plastic, and glass reduce production costs and environmental harm.
This is how E-waste recycling creates a sustainable cycle.
Benefits of E-Waste Recycling
1. Protects the Environment
Recycling prevents harmful chemicals from entering the soil and water. This reduces pollution and improves public health.
2. Saves Natural Resources
Mining gold, copper, and other metals requires huge amounts of energy and causes deforestation. Recycling reduces the need for mining by recovering metals from old devices.
3. Reduces Landfill Waste
E-waste occupies huge space in landfills and releases toxins. Recycling reduces landfill waste and protects land resources.
4. Supports Circular Economy
Recovered materials are reused in new products. This creates a circular and sustainable waste cycle.
5. Creates Jobs and Business Opportunities
Recycling centers, refurbishing units, and repair services create local jobs worldwide.
What Consumers Can Do to Reduce E-Waste
1. Repair Instead of Replace
Try fixing laptops or phones before buying a new device.
2. Buy Durable Products
Choose brands that offer long software updates and strong build quality.
3. Recycle Old Gadgets
Use official recycling points or buy-back programs instead of throwing devices away.
4. Donate Working Devices
Old laptops and phones can be donated to schools or charities.
5. Avoid Hoarding Old Electronics
Many people keep old phones at home. Proper disposal helps reduce E-waste.
Conclusion
E-waste recycling is essential for a cleaner and safer planet. Our laptops, phones, and smartwatches contain valuable materials that should not end up in landfills. Recycling helps recover metals, reduces pollution, and supports sustainable waste management. The entire process—from collection to material recovery—ensures that harmful substances do not damage the environment. By choosing to recycle and reuse electronics, consumers play a major role in protecting natural resources. As technology continues to evolve, responsible E-waste management becomes even more important for future generations.
FAQs
Q.1. What is E-waste recycling?
E-waste recycling is the process of collecting and treating old electronic devices to recover useful materials.
Q.2. Why is E-waste harmful?
It contains toxic chemicals that can pollute soil, water, and air if not disposed safely.
Q.3. Which devices need recycling?
Laptops, phones, smartwatches, tablets, chargers, and batteries should all be recycled.
Q.4. Can old phones and laptops be reused?
Yes, they can be repaired, refurbished, or donated before recycling.
Q.5. Where can people recycle devices?
At official recycling centers, brand buy-back programs, or government-approved collection points.